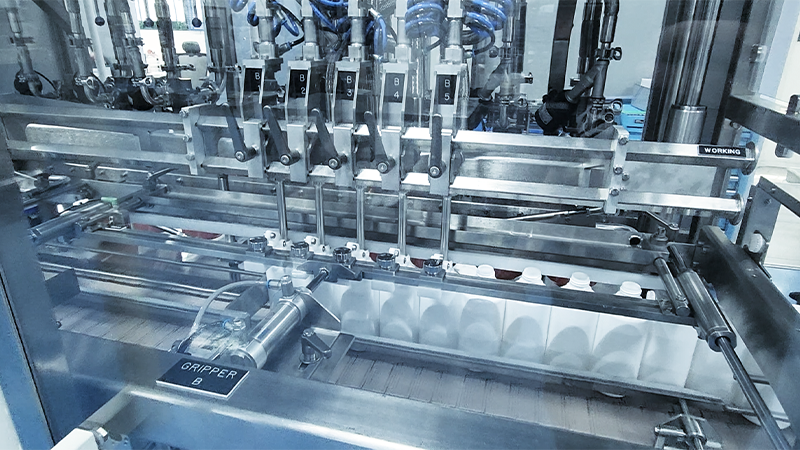
A Comprehensive Guide to Food Filling Machines: In the highly regulated and competitive world of food manufacturing, the efficiency, precision, and hygiene of your production line are critical factors that determine your operation’s success. Food filling machines, which are at the heart of many food packaging processes, play an essential role in ensuring products are accurately dispensed and packaged with minimal waste and contamination. These machines are designed to handle various product types—liquids, solids, semi-solids, and powders—requiring different technical solutions to achieve optimal results.
Watch the machines in action:
- Spirits Filling & Bottling Machines
- Fast and hygienic complete packaging lines for Gummies and Candies
- Condiment & Sauce Filling Machines
- Honey Filling & Bottling Machine
- Soft Drink Filling & Packaging Machines
- Complete turnkey buckets packaging line for food
In this in-depth guide, we’ll discuss the technical aspects of food filling machines, how they work, and the critical factors engineers must consider when selecting the right machine for their application. We will also delve into specific requirements for filling liquid and solid products, exploring how different filling technologies work best in different scenarios.
Liquid, Paste, Solid, and Powder Product Considerations: Engineering Insights
When it comes to selecting the right food filling machine, understanding the specific engineering requirements for different product types—liquids, pastes, solids, and powders—is essential for achieving optimal results. Each category presents unique challenges that require specialized equipment and technology to ensure accurate, efficient, and hygienic filling.
TYPES OF FOOD FILLING MACHINES
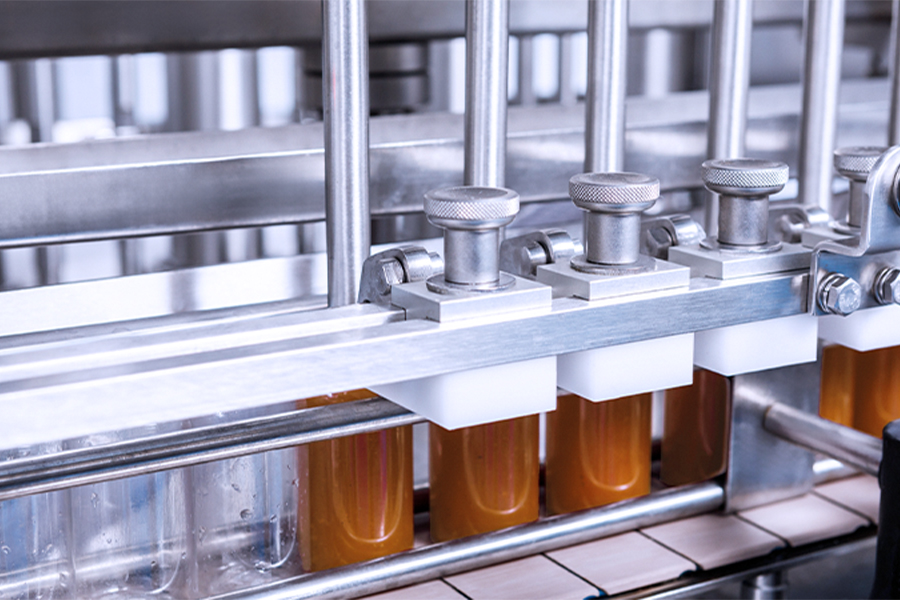

Food filling machines are categorized based on the type of product they handle and the method they use to fill containers. These machines are also distinguished by their level of automation—manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic systems. Here’s a closer look at the primary categories:
Technical Overview: Liquid filling machines are designed to handle liquids of various viscosities, from water to thick sauces and oils. Depending on the product’s properties, different technologies are employed, such as:
- Gravity Fillers: Ideal for low-viscosity, free-flowing liquids such as water or juices.
- Piston Fillers: Use a piston mechanism to dispense thicker liquids, such as sauces, creams, or pastes.
- Pump Fillers: Use a variety of pumps for liquids with more challenging flow properties.
- Overflow Fillers: Provide visually consistent fill levels, perfect for beverages where appearance matters.
Liquid Filling Machines
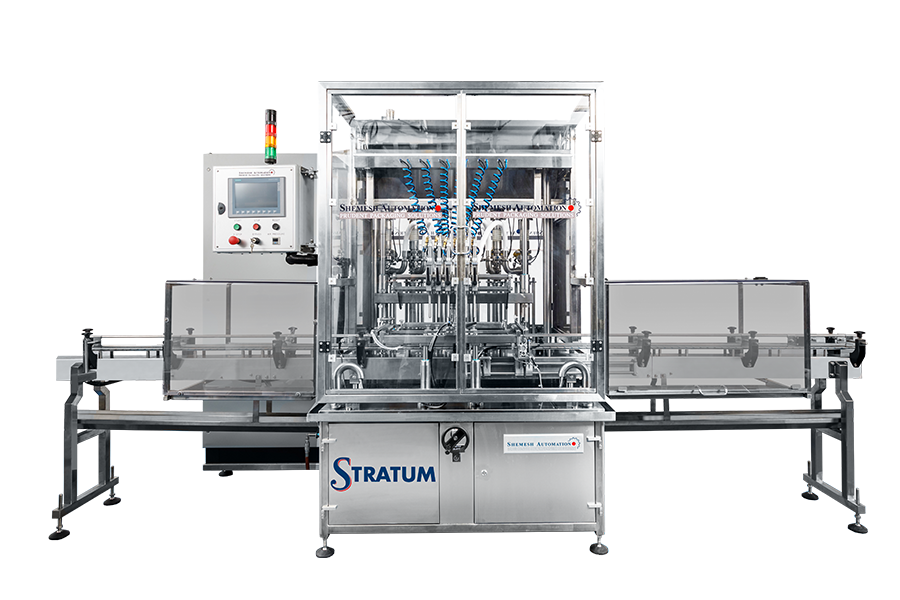

Liquid filling machines must be engineered to handle a variety of liquid types, from thin, water-like products to highly viscous syrups and oils. The product’s viscosity, foaming tendency, and any temperature sensitivity directly impact the design of the filling system.
Foaming Liquids: Products such as carbonated beverages or protein-rich liquids are prone to foaming during filling. To minimize foam formation, machines may use:
- Laminar Flow Nozzles: These nozzles reduce turbulence as the liquid enters the container, ensuring smooth and controlled filling.
- Bottom-Up Filling: In some applications, the nozzle is inserted into the container, filling from the bottom up to reduce splashing and foam generation. This technique is crucial for delicate liquids like carbonated drinks or low-surface-tension products.
- Vent Tubes or Overflow Fillers: These systems allow excess product to overflow or vent, ensuring a consistent fill level for visually sensitive products.
- Temperature-Sensitive Liquids: For products that change viscosity based on temperature (e.g., oils that thicken when cold), filling systems must incorporate temperature control technologies.
- Heated Jackets: Machines equipped with heated jackets keep products at an optimal temperature during filling, ensuring consistent flow rates.
Thermal Sensors and Control Systems:Integrated into the filling machine to maintain precise product temperature, these sensors ensure the product maintains its flow characteristics during the entire filling process.
Precision and Control for Viscosity: Liquid fillers often utilize volumetric or mass flow meters to accurately control the volume of product dispensed. For highly viscous liquids like honey or oils, positive displacement pumps or gear pumps are typically employed, offering consistent and accurate dosing regardless of the liquid’s flow resistance.
Solid Filling Machines

Filling machines designed for solid products, such as granular materials or particulates, must address specific challenges, including variations in product size, density, and flow characteristics. These systems must ensure accurate dispensing while preventing product damage, minimizing spillage, and reducing dust formation. Common examples of such products include:
- Flowability and Bulk Density: Different solids exhibit varying flow behaviors, from free-flowing grains like rice to sticky, cohesive solids such as dried fruits.
- Volumetric Fillers: For free-flowing solids, volumetric cup systems or auger fillers are often used. Volumetric fillers rely on predefined volume compartments that release the product into the container once full.
- Weigh Fillers: For more sensitive or expensive products, such as nuts or confectionery, net weigh filling machines are employed. These machines use precise load cells to weigh the product before it is dispensed, ensuring the exact amount is packaged without excess.
- Product Fragility: Handling fragile products like potato chips or delicate candies requires special consideration to avoid breakage during the filling process.
- Vibratory Feeders: These feeders gently move the product along vibratory trays, reducing the likelihood of damage.
- Slow-Speed Conveyors: Integrated with robotic or automated handling systems, these conveyors carefully transport products to the filling point, preserving their structure.
Dust Control for Fine Particles
For small, dust-generating products such as flour or powdered sugar, engineers need to consider dust collection and extraction systems.
- Enclosed Fill Heads and Vacuum Systems: These systems contain the product within a sealed environment and extract dust as it is generated, improving cleanliness and reducing airborne particles.
- Antistatic Systems: In some applications, antistatic systems are used to prevent fine particles from clinging to surfaces and creating buildup or contamination in the machine.
Paste and Semi-Solid Filling Machines

Paste and semi-solid products present unique challenges due to their high viscosity, stickiness, and sometimes their inclusion of particulates (like fruit chunks or pieces). These products require filling machines designed to handle resistance to flow and potential clogging while maintaining precise and consistent filling.
High Viscosity and Flow Resistance
Products like peanut butter, honey, tahini, and thick sauces require filling machines that can handle the resistance these high-viscosity products present.
- Piston Fillers: Piston fillers are one of the most reliable solutions for high-viscosity products. These machines use a piston to draw in the product and then push it into the container with consistent pressure. Engineers can adjust the piston’s stroke length to control the fill volume with high accuracy.
- Technical Advantage: The piston mechanism allows for precise control over each filling cycle, making it particularly useful for products that resist flow or may have varying consistencies throughout the batch.
- Positive Displacement Pumps: For continuous product flow, positive displacement pumps are highly effective. These pumps move a fixed amount of product with each rotation, ensuring consistency regardless of the product’s viscosity. These systems are especially beneficial for highly viscous products like pastes or semi-solid sauces.
- Technical Advantage: Positive displacement pumps are ideal for handling both thin and thick paste-like materials, allowing for smooth operation even with products containing particulates.
Handling Inclusions and Particulates
Certain paste products, such as fruit-based yogurts or sauces containing vegetable chunks, require specialized filling machines that can handle both the liquid base and the solid inclusions without damaging or separating them.
- Large-Diameter Nozzles: Paste filling machines are often equipped with wide-diameter nozzles to accommodate larger particulates, ensuring the smooth transfer of both the paste and the inclusions without clogging.
- Technical Advantage: This feature allows for seamless filling of products with a mix of solid inclusions, ensuring even distribution of ingredients without damaging the particulates.
- Dual-Valve Systems: These systems use separate valves to control the flow of the base product and the solid inclusions. The dual-valve system ensures an even and precise fill, with both the liquid paste and particulates entering the container simultaneously and in the correct proportion.
- Technical Advantage: This ensures uniform distribution of inclusions throughout the product, which is critical for consumer satisfaction and product quality consistency.
Precision Filling for Semi-Solid Products
Semi-solid products, such as custards, creams, and gels, can present challenges in terms of maintaining consistent volume and avoiding product waste. These types of products benefit from the precision offered by advanced servo-driven filling systems.
- Servo-Driven Fillers: These systems use servo motors to control the pistons, pumps, or other filling mechanisms with extreme precision. This allows for highly accurate, repeatable fill volumes, which is essential for maintaining consistency, especially for semi-solid products that may vary in density or texture.
- Technical Advantage: Servo-driven fillers enable fine-tuning of fill speeds and volumes, which minimizes product waste and ensures precise, uniform filling.
Powder Filling Machines

Powder products, due to their light weight and propensity to form dust clouds, require specialized filling solutions that maintain product accuracy while minimizing waste and environmental hazards.
Flowability and Dispersion Control
Powder products such as spices, flour, or protein powders often need filling systems that can control fine particles without causing blockages or product loss.
- Auger Fillers: These fillers use a rotating auger screw to precisely measure and dispense powder into containers. Auger fillers are commonly used for free-flowing powders and maintain high levels of accuracy and consistency.
- Vacuum Fillers: For very fine powders or dusty products, vacuum fillers use air pressure differentials to transport the powder into the container without creating dust clouds or spillage.
Handling Hygroscopic Powders
Certain powders, such as salt or protein powders, tend to absorb moisture from the air. Hygroscopic products require specialized filling machines with integrated moisture control systems, such as:
- Desiccant Systems: Some machines are equipped with desiccants to control moisture levels and prevent product degradation during filling.
- Sealed Conveying Systems: For highly sensitive powders, the conveying process is often fully enclosed to protect the product from humidity and external contaminants.
Precision and Automation
Powders require precision filling due to their tendency to compact or clump. Modern powder filling machines often include:
- Servo Motors: These offer precise control over the auger’s rotation, allowing engineers to fine-tune the amount of product dispensed for each fill cycle.
- Dust Extraction Systems: Ensure that fine powders don’t become airborne during filling, maintaining a clean working environment and ensuring product consistency.
How Food Filling Machines Work
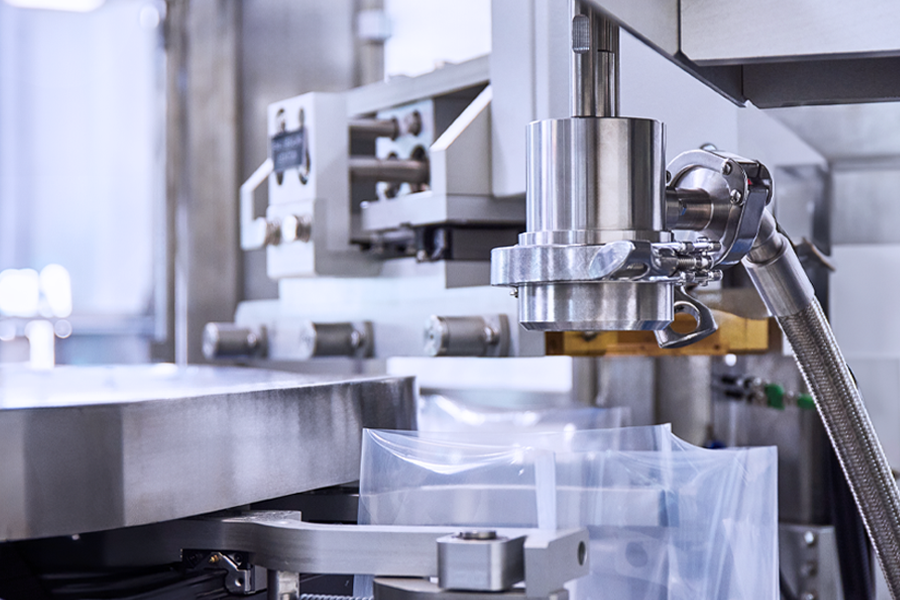

The operation of food filling machines varies based on their automation level—manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic—and their design. Here’s a breakdown of how they work at each level:1. Manual Food Filling Machines
Manual systems involve mechanical or pneumatic controls, best for small-batch operations.
2. Semi-Automatic Food Filling Machines
These systems automate the filling process but require manual container handling before and after filling.
3. Automatic Food Filling Machines
Fully automated machines perform the entire process from container transport to filling and sealing.
The Crucial Factors in Food Packaging Machine Selection
When selecting food filling machines, engineers must consider the following:
- Product Characteristics: Whether liquid, solid, paste, or powder.
- Filling Accuracy: Gravimetric or volumetric systems.
- Hygiene and Cleanability: Compliance with food-grade materials and CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems.
- Automation and Integration: Ensuring seamless integration with upstream and downstream processes.
Advanced Components in Automatic Systems
- Multi-Nozzle Systems: Allow simultaneous filling of multiple containers, improving throughput for high-demand products.
- Servo-Driven Systems: Offer accurate, repeatable control of filling volumes, making them ideal for high-value or sensitive products.
- PLC Controls: Facilitate easy adjustment of fill parameters, product recipes, and machine speeds, ensuring flexibility for different product lines.
Conclusion
Choosing the right food filling machine is a critical decision for engineers. Understanding the technical aspects of these machines ensures efficiency, accuracy, and hygiene in food production. Whether handling liquids, solids, semi-solids, or powders, the correct machine can enhance production, minimize waste, and ensure product quality.
For more information on our Automated Packaging Machinery, contact us today to discuss how we can fulfill your unique packaging requirements.
Join us on LinkedIn to stay updated with our latest news and discover our innovations in filling, capping, and sealing solutions.